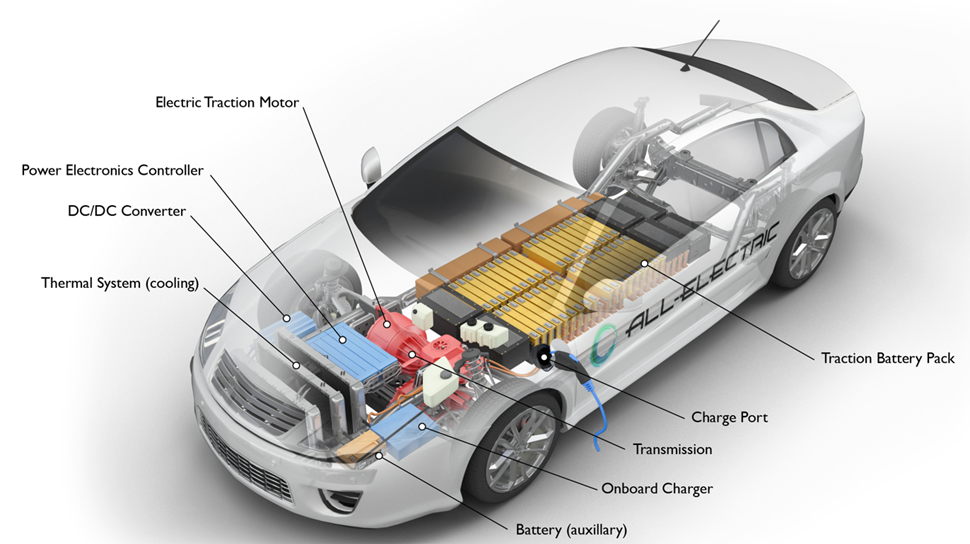
Key Components of EV are:
Auxiliary Battery: In an electric drive vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to vehicle accessories.
Charge port: The charge port allows the vehicle to connect to an external power supply in order to charge the traction battery pack.
DC/DC converter: This device converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower-voltage DC power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Electric traction motor: Using power from the traction battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle’s wheels. Some vehicles use motor generators that perform both the drive and regeneration functions. It can be a DC or AC type. However, AC motors are more common.
Onboard charger: Takes the incoming AC electricity supplied via the charge port and converts it to DC power for charging the traction battery. It also communicates with the charging equipment and monitors battery characteristics such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge while charging the pack.
Power electronics controller: This unit manages the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery, controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it produces.
Thermal system (cooling): This system maintains a proper operating temperature range of the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components.
Traction battery pack: Stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor.
Transmission (electric): The transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric traction motor to drive the wheels.
Inverter – Converts the electric current form of Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC)
How an electric car works:
- When we charge the battery, it stores electrical energy. The stored energy is used to power the electric motor.
- The flow of electrical energy to the motor is managed by the controller.
- The controller controls the flow of electricity based on the data received from the accelerator pedal.
- The electric motor draws energy from the battery and transforms it into mechanical energy.
- The transmission then transfers the mechanical energy from the motor to the wheels.
- The energy produced by braking or slowing the vehicle is returned to the battery pack & known as regenerative breaking.
- The battery pack can be charged using the charging port. The onboard charger converts AC to DC.
- An EV also have an auxiliary battery that powers the vehicle’s accessories.