Mainly four types of electric vehicles are available in market:
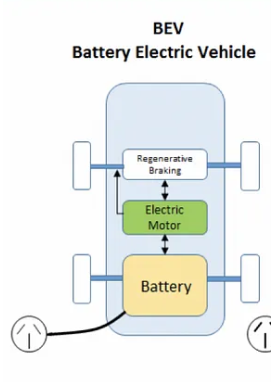
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV): These Evs are Fully powered by electricity. The electricity used to drive the vehicle is stored in a large battery pack which can be charged by plugging into the electricity grid. The charged battery pack then provides power to electric motors to run the electric car.
The power for the electric motor is converted from the DC Battery to AC with the help of Inverter. When the accelerator is pressed, a signal is sent to the controller. The controller adjusts the speed of the vehicle by changing the frequency of the AC power to the motor. If the brake is pressed, or the electric car is decelerating, the motor becomes an alternator and produces power, which in turn is sent back to the battery to charge it (Regenerative Breaking)
Examples of BEV:
MG ZS EV , TATA Nexon, TATA Tigor, TATA Tiago
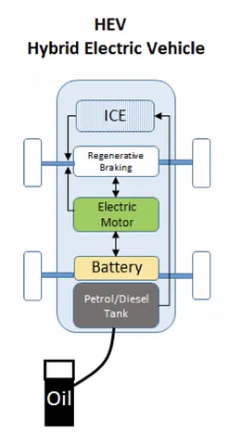
Hybrid Electric Vehicle:
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV): The vehicle uses both the internal combustion engine and the battery-powered motor. The petrol engine is used to drive the vehicle as well as to charge the battery when the battery is discharged. HEV doesn’t have external plug to charge the battery.
The engine gets energy from fuel, and the motor gets electricity from batteries. The transmission is rotated simultaneously by both engine and electric motor. This then drives the wheels
Examples of HEV:
Maruti Suzuki Grand Vitara, Toyota Urban Cruiser Hyryder, Honda City Ehev
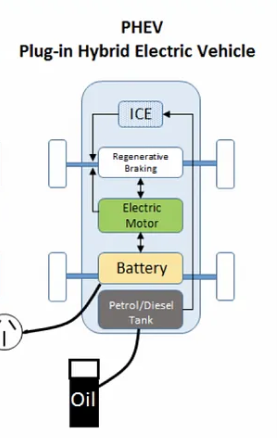
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV): PHEV has both an internal combustion engine and a battery pack which is charged from an external socket. The vehicle’s battery is charged with electricity instead of the engine.
PHEVs initially starts in all-electric mode and runs on the battery until their battery is discharged. Once the battery gets drained, the engine takes over, and the vehicle operates as a conventional, non-plug-in hybrid. PHEVs can be charged by plugging into an outside electric power source, engine, or regenerative braking.
Examples of PHEV:
Volvo XC90 Recharge, BMW 7 Series
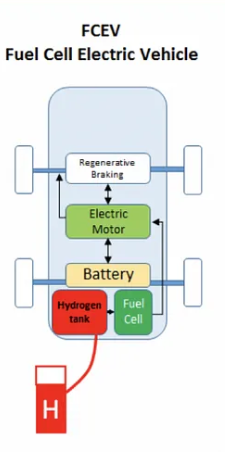
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV): Electric energy is produced from chemical energy. For example, a hydrogen FCEV. They employ ‘fuel cell technology’ to generate the electricity required to run the vehicle. The chemical energy of the fuel is converted directly into electric energy.
Examples of FCEV:
Toyota Mirai